Welcome to the Population Community and Ecosystem Worksheet, an essential resource for understanding the intricate relationships between organisms and their environment. This comprehensive guide delves into the fundamental concepts of population, community, and ecosystem, exploring their characteristics, interactions, and the profound impact humans have on these delicate systems.
Throughout this worksheet, we will embark on a journey of discovery, uncovering the complexities of ecological interactions and the critical role of conservation in preserving the balance of nature. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of the natural world and empower you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about our planet’s future.
Population
A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area and interact with each other.
The characteristics of a population include its size, density, distribution, and age structure.
Examples of different types of populations include a population of deer in a forest, a population of fish in a lake, or a population of bacteria in a petri dish.
- Size: The number of individuals in a population.
- Density: The number of individuals per unit area or volume.
- Distribution: The spatial arrangement of individuals within a population.
- Age structure: The proportion of individuals in different age groups.
Community

A community is a group of different species that live in the same area and interact with each other.
The difference between a population and a community is that a population is a group of organisms of the same species, while a community is a group of organisms of different species.
Examples of different types of communities include a community of plants and animals in a forest, a community of fish and invertebrates in a coral reef, or a community of bacteria and fungi in a soil.
- Species diversity: The number of different species in a community.
- Species richness: The relative abundance of different species in a community.
- Trophic structure: The feeding relationships between different species in a community.
Ecosystem
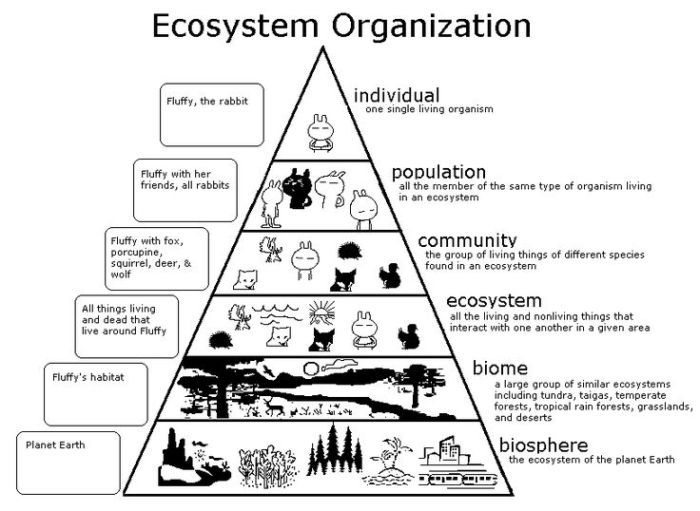
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms and their physical environment.
The difference between a community and an ecosystem is that a community is a group of organisms of different species, while an ecosystem is a community of organisms and their physical environment.
Examples of different types of ecosystems include a forest ecosystem, a grassland ecosystem, or an aquatic ecosystem.
- Abiotic factors: The physical and chemical factors that affect an ecosystem, such as temperature, light, and water.
- Biotic factors: The living organisms in an ecosystem.
- Energy flow: The movement of energy through an ecosystem.
- Nutrient cycling: The movement of nutrients through an ecosystem.
Interactions within Populations, Communities, and Ecosystems

There are many different types of interactions that can occur within populations, communities, and ecosystems.
Interactions within Populations
- Competition: The interaction between individuals of the same species for limited resources.
- Predation: The interaction between a predator and its prey.
- Symbiosis: A close relationship between two different species.
Interactions within Communities
- Competition: The interaction between individuals of different species for limited resources.
- Predation: The interaction between a predator and its prey.
- Symbiosis: A close relationship between two different species.
- Mutualism: A symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit.
- Commensalism: A symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other is unaffected.
- Parasitism: A symbiotic relationship in which one species benefits and the other is harmed.
Interactions within Ecosystems
- Producer-consumer interactions: The interaction between producers (organisms that make their own food) and consumers (organisms that eat other organisms).
- Decomposer-consumer interactions: The interaction between decomposers (organisms that break down dead organisms) and consumers.
- Nutrient cycling: The movement of nutrients through an ecosystem.
Human Impact on Populations, Communities, and Ecosystems
Humans can have a significant impact on populations, communities, and ecosystems.
Human Impact on Populations
- Habitat destruction: The destruction of an organism’s habitat.
- Overexploitation: The harvesting of a species at a rate that exceeds its ability to reproduce.
- Pollution: The introduction of harmful substances into an environment.
- Climate change: The long-term alteration of temperature and typical weather patterns in a place.
Human Impact on Communities
- Habitat destruction: The destruction of an organism’s habitat.
- Overexploitation: The harvesting of a species at a rate that exceeds its ability to reproduce.
- Pollution: The introduction of harmful substances into an environment.
- Climate change: The long-term alteration of temperature and typical weather patterns in a place.
- Invasive species: The introduction of a non-native species into an ecosystem.
Human Impact on Ecosystems, Population community and ecosystem worksheet
- Habitat destruction: The destruction of an organism’s habitat.
- Overexploitation: The harvesting of a species at a rate that exceeds its ability to reproduce.
- Pollution: The introduction of harmful substances into an environment.
- Climate change: The long-term alteration of temperature and typical weather patterns in a place.
- Invasive species: The introduction of a non-native species into an ecosystem.
- Nutrient pollution: The introduction of excess nutrients into an ecosystem.
Conservation of Populations, Communities, and Ecosystems
It is important to conserve populations, communities, and ecosystems because they provide us with a number of benefits, including food, water, and air.
Importance of Conserving Populations
- Populations provide us with food, water, and other resources.
- Populations help to regulate the environment.
- Populations are a source of genetic diversity.
Importance of Conserving Communities
- Communities provide us with food, water, and other resources.
- Communities help to regulate the environment.
- Communities are a source of genetic diversity.
- Communities provide us with recreational opportunities.
Importance of Conserving Ecosystems
- Ecosystems provide us with food, water, and other resources.
- Ecosystems help to regulate the environment.
- Ecosystems are a source of genetic diversity.
- Ecosystems provide us with recreational opportunities.
- Ecosystems are essential for human health and well-being.
Questions Often Asked: Population Community And Ecosystem Worksheet
What is the difference between a population and a community?
A population refers to a group of organisms of the same species living in a particular area, while a community encompasses all the populations of different species that inhabit the same area and interact with each other.
How do interactions within an ecosystem contribute to its stability?
Interactions such as competition, predation, and symbiosis maintain a balance within ecosystems, preventing any one species from dominating and ensuring the long-term survival of the entire community.
Why is conserving ecosystems important?
Ecosystems provide essential services such as clean air, water, and food, and their conservation is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and mitigating the impacts of climate change.
