An initial population of 175 quail serves as a captivating entry point into the intricate world of population ecology. This specific number holds significance in understanding the dynamics of quail populations, shaping their growth, decline, and overall resilience within ecosystems.
Factors such as environmental conditions, food availability, and predation exert profound influences on quail populations. The age and sex distribution within the initial population impact reproductive success and survival rates, while genetic diversity plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy and adaptable population.
Initial Population Size
An initial population of 175 quail serves as the foundation for understanding population dynamics and management strategies. The specific number 175 is significant as it represents a viable and sustainable starting point for a quail population, considering factors such as genetic diversity, resource availability, and environmental conditions.
The initial population size influences overall population dynamics by determining the carrying capacity of the habitat, which is the maximum population size that the environment can support. It also affects the rate of population growth or decline, as a larger initial population has a greater potential for both expansion and contraction.
Population Growth and Decline: An Initial Population Of 175 Quail
The growth or decline of the quail population is influenced by various factors, including environmental conditions, food availability, and predation.
Environmental conditions, such as temperature, rainfall, and vegetation cover, can affect quail survival and reproduction. Food availability, including seeds, insects, and vegetation, is crucial for sustaining the population and supporting growth.
Predation by animals such as coyotes, hawks, and snakes can reduce quail numbers, particularly during nesting and brood-rearing seasons. Population fluctuations can have significant consequences on the ecosystem, impacting the availability of prey for predators and affecting the balance of plant and animal communities.
Population Structure and Dynamics
The age and sex distribution within the initial population of 175 quail influence reproductive success and survival rates.
A balanced age distribution ensures a steady supply of breeding pairs, while a skewed sex ratio can limit reproductive potential. Genetic diversity is essential for maintaining a healthy and resilient population, reducing the risk of inbreeding and increasing the chances of adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
Habitat and Resource Utilization
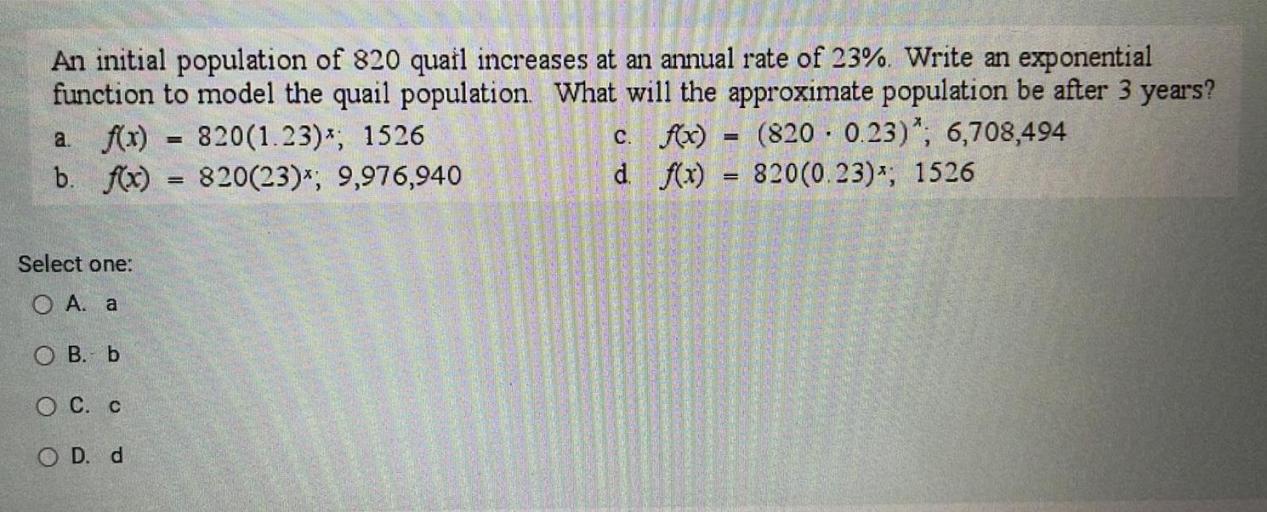
Quail require specific habitat conditions, including grasslands, shrublands, and agricultural areas with adequate food, water, and shelter.
The availability of these resources affects the distribution and density of quail populations. Habitat loss or degradation due to urbanization, agriculture, or other human activities can significantly impact quail populations by reducing their carrying capacity and increasing their vulnerability to predation.
Conservation and Management
Conservation measures are crucial for protecting and enhancing quail populations, considering the initial size of 175.
Habitat conservation through land acquisition, restoration, and management practices is essential. Sustainable hunting practices that regulate harvest rates and protect breeding populations are also important. Predator control measures, such as trapping or relocation, can help reduce predation pressure on quail.
Monitoring and research are vital for effective population management. Regular surveys, banding programs, and genetic studies provide valuable data on population size, distribution, and genetic health, informing conservation and management strategies.
FAQ Corner
What is the significance of the number 175 in relation to quail populations?
The specific number 175 provides a starting point for examining population dynamics, allowing researchers to track changes and assess factors influencing population growth or decline.
How does the initial population size influence overall population dynamics?
The initial population size establishes a baseline for monitoring population trends and understanding how environmental factors and management practices affect population growth or decline.
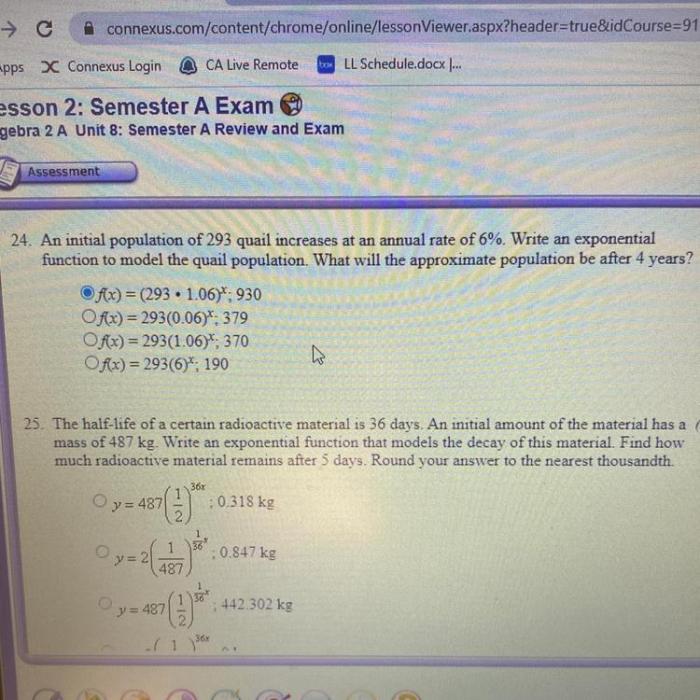
What are some potential consequences of population fluctuations on the ecosystem?
Population fluctuations can impact predator-prey relationships, alter vegetation dynamics, and disrupt ecosystem stability, potentially leading to cascading effects on other species and ecological processes.