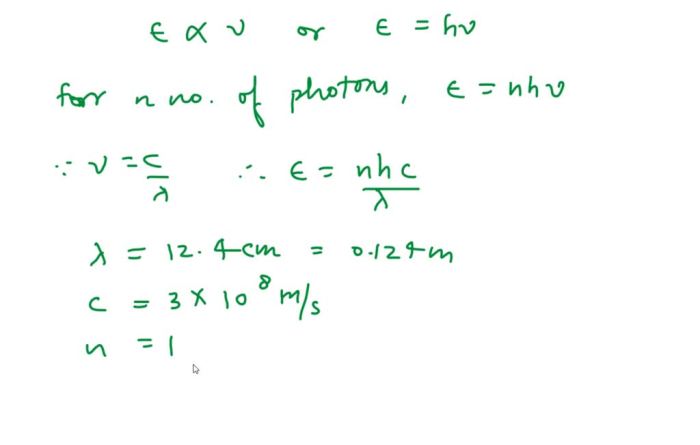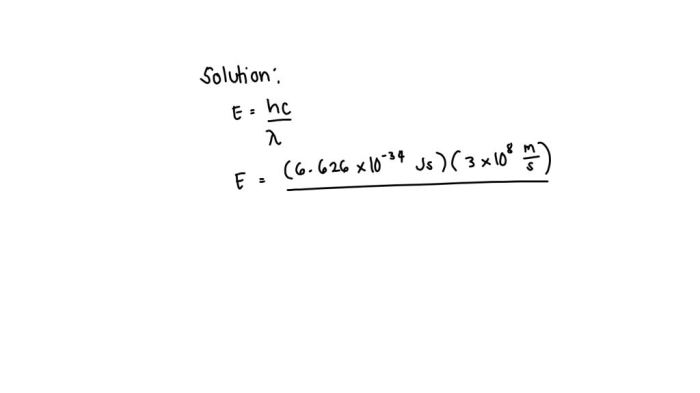Microwave ovens emit microwave energy with a wavelength of 2.45 GHz, which is the specific wavelength range used in ovens to heat food efficiently. This wavelength range is significant because it interacts with food molecules, causing them to vibrate and generate heat through a process called dielectric heating.
The history of microwave ovens dates back to the early 20th century, with the first commercial microwave oven introduced in 1947. Since then, microwave ovens have become a common household appliance due to their convenience and efficiency in heating food.
Microwave Energy Basics: Microwave Ovens Emit Microwave Energy With A Wavelength Of

Microwave energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength range typically between 1 millimeter and 1 meter. It falls within the radio frequency (RF) band of the electromagnetic spectrum, specifically in the frequency range of 300 MHz to 300 GHz.
The history of microwave ovens can be traced back to the early 20th century when scientists were experimenting with high-frequency electromagnetic waves. In 1945, Percy Spencer, an American engineer working for Raytheon, accidentally discovered the ability of microwave energy to heat food while working on a magnetron, a device used in radar systems.
Wavelength of Microwave Energy, Microwave ovens emit microwave energy with a wavelength of
Microwave ovens typically operate at a wavelength of 12.24 centimeters (2.45 GHz frequency), which is within the microwave energy range of 1 millimeter to 1 meter. This specific wavelength was chosen because it is effectively absorbed by water molecules, which are abundant in food.
The wavelength of microwave energy is significant for heating food because it matches the resonant frequency of water molecules. When microwave energy is directed at food, the water molecules align themselves with the oscillating electric field of the microwaves and rapidly rotate, causing friction and generating heat.
Mechanism of Microwave Heating
Microwave heating is a process known as dielectric heating. Dielectric materials, such as water, have the ability to store electrical energy when exposed to an alternating electric field. When microwave energy is applied to a dielectric material, the molecules align themselves with the field and rotate rapidly, causing friction and generating heat.
In a microwave oven, the food is placed in a cavity surrounded by a magnetron, which generates microwaves. The microwaves penetrate the food and interact with the water molecules, causing them to vibrate and generate heat. This heat is then transferred to the surrounding food, cooking it evenly and quickly.
Safety Considerations
Microwave ovens are generally safe to use when operated properly. However, there are potential safety concerns that should be considered:
- Overheating:Food can overheat in a microwave oven, especially if it is cooked for too long or at too high a power level. Overheating can cause food to burn or catch fire.
- Radiation leakage:Microwave ovens are designed to prevent radiation leakage, but it is possible for small amounts of microwave energy to escape through gaps in the door or other parts of the oven. Prolonged exposure to microwave radiation can be harmful to health.
- Burns:The food and cookware in a microwave oven can become very hot, and touching them without proper protection can cause burns.
To ensure safe microwave operation, follow these guidelines:
- Use the oven only for its intended purpose.
- Do not operate the oven if the door is damaged or not properly closed.
- Do not place metal objects in the oven.
- Use microwave-safe cookware.
- Cook food for the recommended time and power level.
- Allow the food to cool before handling.
Applications of Microwave Ovens
Microwave ovens are primarily used for heating and cooking food. However, microwave energy has a wide range of applications beyond food preparation, including:
- Industrial heating:Microwave energy can be used to heat materials quickly and efficiently in industrial processes, such as drying, curing, and welding.
- Medical applications:Microwave energy is used in medical devices such as microwave ablation systems, which use microwaves to destroy cancerous tissue.
- Scientific research:Microwave energy is used in scientific research to study the properties of materials and to develop new technologies.
FAQ
What is the wavelength of microwave energy used in ovens?
Microwave ovens emit microwave energy with a wavelength of 2.45 GHz.
How do microwave ovens heat food?
Microwave ovens heat food through a process called dielectric heating, where microwave energy interacts with food molecules, causing them to vibrate and generate heat.
Are microwave ovens safe to use?
Microwave ovens are safe to use when operated properly. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for safe use to minimize the risk of exposure to microwave radiation and burns.