Select the true statements about how flu vaccines are produced. – Embark on a journey into the realm of flu vaccine production, where scientific advancements collide with the unwavering pursuit of public health. From the intricacies of cell culture to the meticulous selection of influenza strains, we delve into the complexities of vaccine manufacturing, unraveling the true statements that govern this vital process.
The production of flu vaccines is a symphony of scientific expertise and regulatory oversight, guided by the unwavering commitment to safeguarding communities from the relentless threat of influenza.
Production Methods
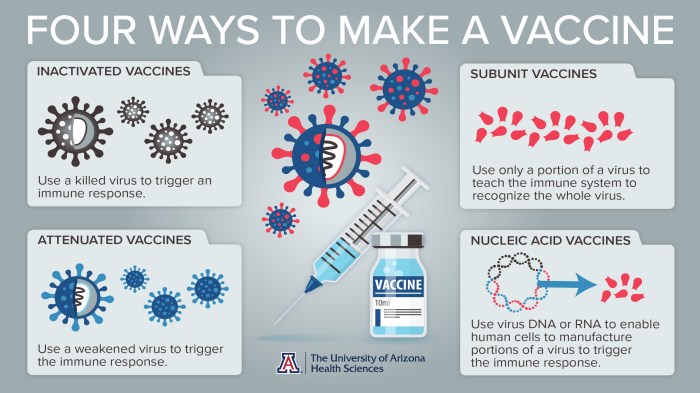
Flu vaccines are produced using various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Cell Culture
- Involves growing the influenza virus in cell cultures.
- Allows for precise control of the virus and production process.
- Produces high-yield vaccines with reduced risk of contamination.
Egg-based Production
- Involves injecting the influenza virus into fertilized chicken eggs.
- A traditional and widely used method.
- Produces large quantities of vaccine but has a higher risk of contamination.
Recombinant Technology
- Uses genetic engineering to produce viral proteins.
- Allows for the production of specific viral components.
- Can reduce the risk of contamination and produce vaccines faster than traditional methods.
Vaccine Components
Flu vaccines contain several key components that work together to protect against influenza:
Viral Antigens
- Fragments of the influenza virus that trigger the immune system.
- Typically include hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) proteins.
- Help the immune system recognize and attack the influenza virus.
Adjuvants, Select the true statements about how flu vaccines are produced.
- Substances that enhance the immune response to the vaccine.
- Examples include aluminum salts and squalene.
- Increase antibody production and the duration of immunity.
Preservatives
- Chemicals that prevent the growth of bacteria and fungi in the vaccine.
- Examples include thimerosal and formaldehyde.
- Ensure the safety and stability of the vaccine.
Strain Selection
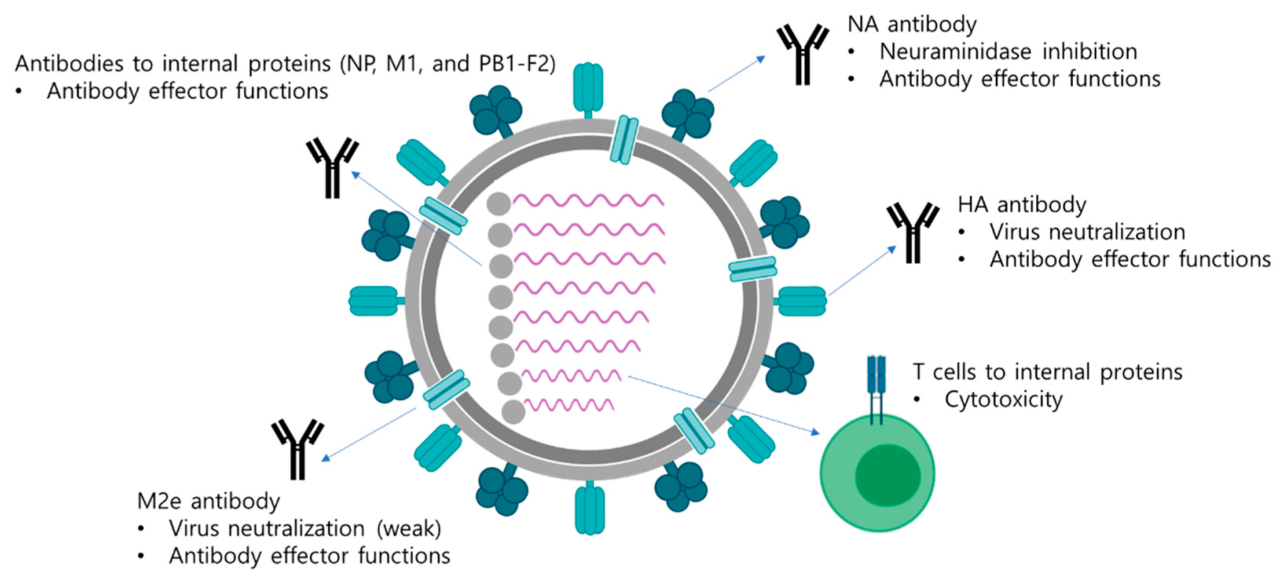
The selection of influenza strains for vaccine production is a critical process:
Role of the World Health Organization (WHO)
- WHO monitors influenza activity globally and recommends the strains to be included in the vaccine each year.
- Based on surveillance data and genetic analysis.
- Ensures that the vaccine protects against the most prevalent strains.
Challenges and Considerations
- Influenza viruses evolve rapidly, making strain selection difficult.
- Need to anticipate the strains that will circulate in the upcoming season.
- Factors considered include genetic drift, antigenic shift, and regional variations.
Production Timeline
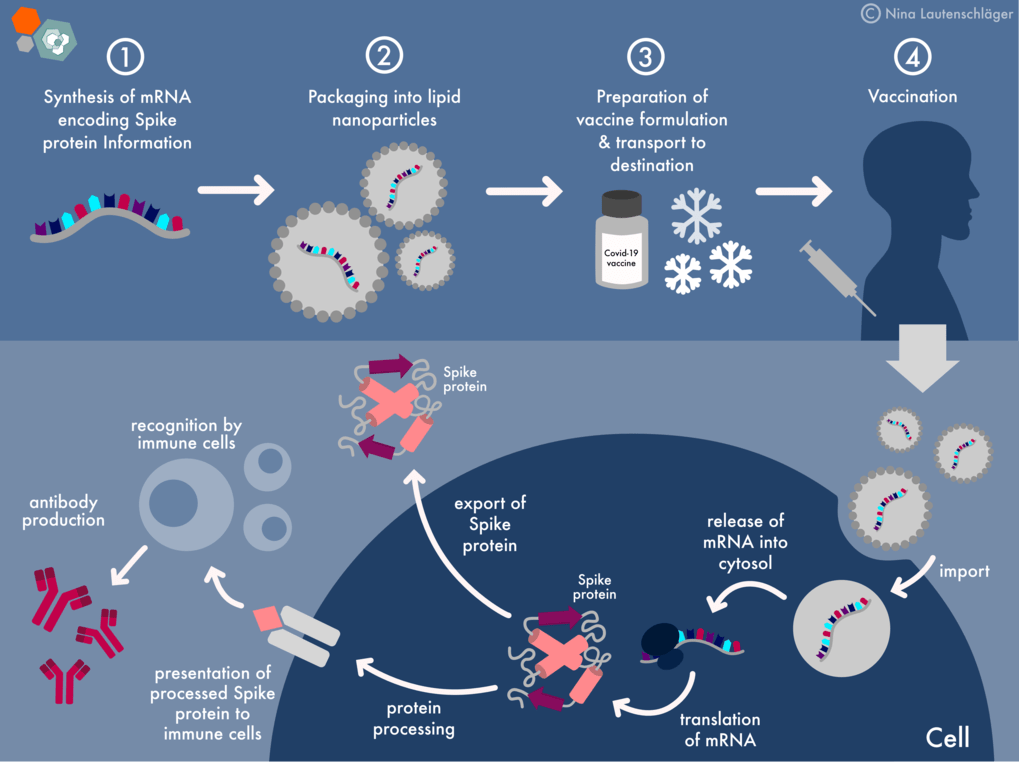
The flu vaccine production process typically follows a timeline:
Spring-Summer: Strain Selection
- WHO recommends the vaccine strains for the upcoming season.
- Manufacturers begin producing seed viruses.
Summer-Fall: Production
- Viruses are grown in cell cultures or eggs.
- Viral antigens are harvested and purified.
- Vaccines are formulated with adjuvants and preservatives.
Fall-Winter: Distribution and Vaccination
- Vaccines are distributed to healthcare providers.
- Vaccination campaigns begin in September or October.
- Optimal time for vaccination is before the flu season.
Quality Control
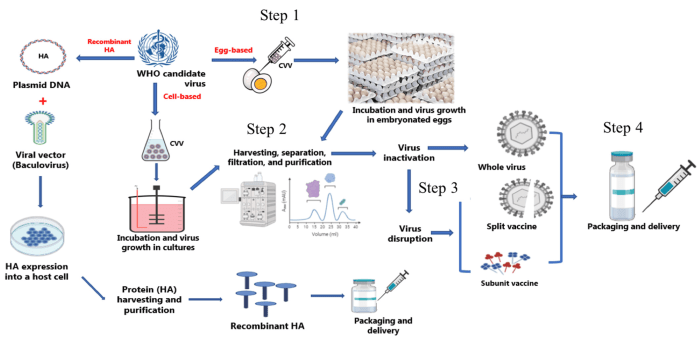
Strict quality control measures ensure the safety and efficacy of flu vaccines:
Testing and Evaluation
- Vaccines are tested for potency, purity, and safety.
- Animal and clinical trials are conducted to assess efficacy and immunogenicity.
- Regular monitoring of vaccine effectiveness during the flu season.
Regulatory Bodies
- Regulatory bodies, such as the FDA and EMA, approve vaccines for use.
- Conduct inspections of manufacturing facilities and review clinical data.
- Ensure compliance with safety and efficacy standards.
Frequently Asked Questions: Select The True Statements About How Flu Vaccines Are Produced.
What are the different methods used to produce flu vaccines?
Flu vaccines are primarily produced using two methods: cell culture and egg-based production. Cell culture involves growing the influenza virus in mammalian cells, while egg-based production utilizes fertilized chicken eggs.
How are influenza strains selected for vaccine production?
The World Health Organization (WHO) plays a crucial role in selecting influenza strains for vaccine production. They monitor global influenza trends and recommend strains that are most likely to circulate during the upcoming flu season.
What are the key components of flu vaccines?
Flu vaccines contain inactivated or weakened influenza viruses, which trigger the body’s immune response without causing illness. They may also include adjuvants to enhance the immune response and preservatives to ensure vaccine stability.