An oil pump is drawing 44 kW, delving into the intricacies of this essential equipment’s power consumption and performance, uncovering factors that influence its efficiency and optimal operation. Dive in and discover how an oil pump’s design, operating conditions, and maintenance practices impact its energy usage and effectiveness.
This comprehensive exploration unveils the pump’s performance characteristics, including flow rate, pressure, and head, and how power consumption plays a crucial role in determining its capacity. We’ll delve into methods for optimizing pump performance and capacity, ensuring alignment with specific application requirements.
Power Consumption and Energy Efficiency
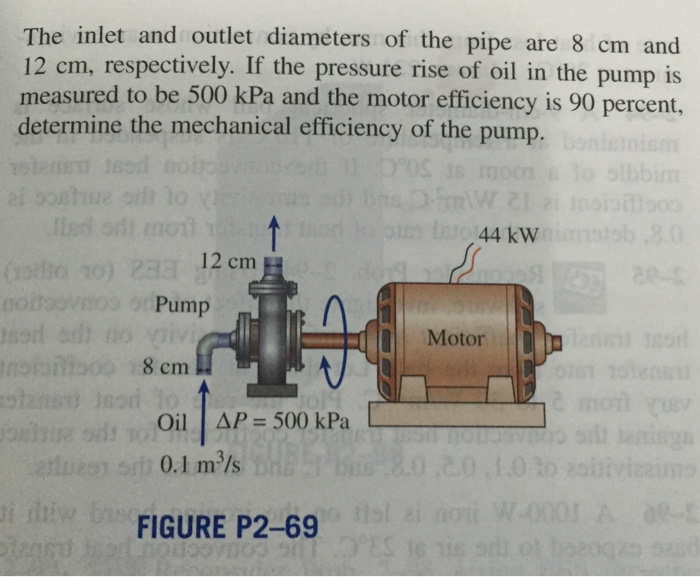
The oil pump’s power consumption of 44 kW is a measure of the electrical energy it requires to operate. Energy efficiency, on the other hand, refers to the pump’s ability to convert this electrical energy into useful work in pumping oil.
Several factors influence the energy efficiency of an oil pump, including:
Pump Design
- Impeller design and efficiency
- Casing design and hydraulic losses
- Materials used and their impact on friction and wear
Operating Conditions
- Flow rate and pressure requirements
- Viscosity and temperature of the oil being pumped
- System losses due to piping, valves, and fittings
Maintenance Practices
- Regular inspection and cleaning to prevent fouling and wear
- Proper lubrication to reduce friction and extend component life
- Monitoring and adjustment of operating parameters to optimize efficiency
Pump Performance and Capacity
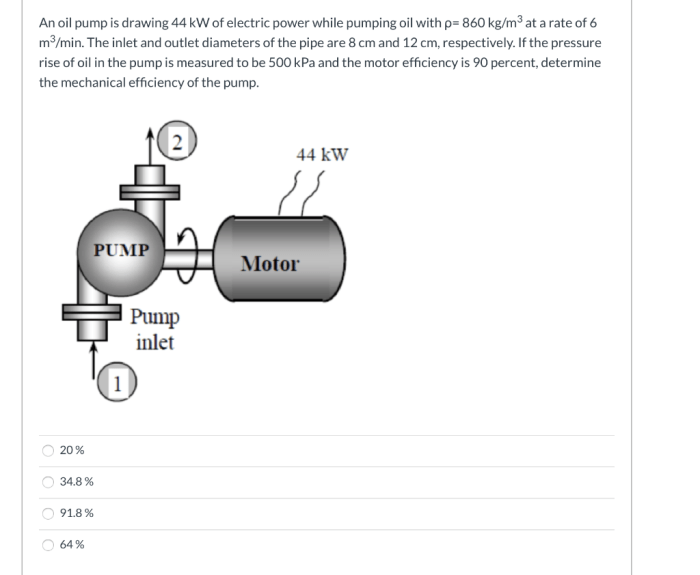
The performance of an oil pump is characterized by its flow rate, pressure, and head. Flow rate refers to the volume of fluid pumped per unit time, pressure is the force per unit area exerted by the fluid, and head is the height to which the fluid is lifted.
Power consumption influences pump performance and capacity, as higher power consumption generally leads to increased flow rate, pressure, and head.
Optimizing Pump Performance and Capacity
Optimizing pump performance and capacity involves matching the pump to the specific application requirements. This includes considering factors such as the required flow rate, pressure, and head, as well as the fluid properties and system constraints. Proper pump selection, installation, and maintenance are crucial for achieving optimal performance and capacity.
Pump Design and Components
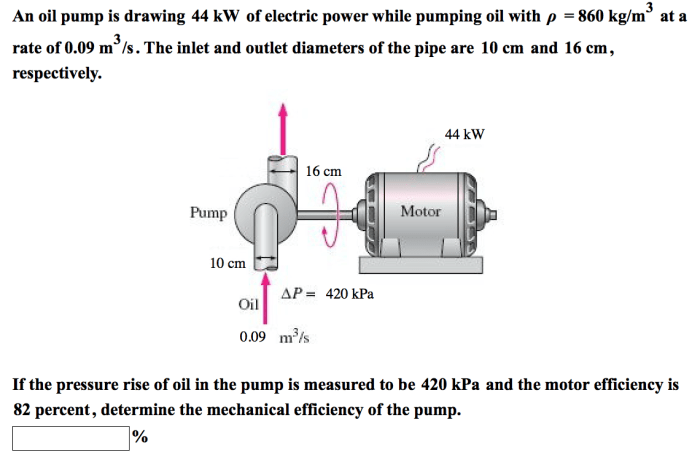
The design of an oil pump plays a crucial role in determining its power consumption and performance. The key components of an oil pump include the impeller, casing, and bearings.
The impeller is the rotating part of the pump that creates the suction and pressure necessary to move the oil. The casing is the stationary part of the pump that surrounds the impeller and directs the flow of oil. The bearings support the impeller and allow it to rotate smoothly.
The efficiency of an oil pump is determined by the design of the impeller and casing. A well-designed impeller will create a smooth flow of oil with minimal turbulence. A well-designed casing will minimize friction losses and ensure that the oil is directed efficiently to the desired location.
Types of Oil Pumps, An oil pump is drawing 44 kw
There are several different types of oil pumps, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The most common types of oil pumps include:
- Gear pumps: Gear pumps use two gears to create suction and pressure. They are simple in design and relatively inexpensive to manufacture. However, they can be noisy and inefficient at high speeds.
- Vane pumps: Vane pumps use a rotor with sliding vanes to create suction and pressure. They are more efficient than gear pumps but can be more expensive to manufacture.
- Centrifugal pumps: Centrifugal pumps use a rotating impeller to create suction and pressure. They are the most efficient type of oil pump but can be more expensive to manufacture than gear or vane pumps.
Electrical Considerations

The electrical requirements for operating an oil pump are crucial for ensuring its efficient and reliable performance. These requirements include voltage, current, and power factor, which directly impact the pump’s operation and energy consumption.
Voltage
The voltage supplied to the oil pump must match the voltage rating of the motor. Operating the pump at a voltage below its rated voltage can lead to reduced performance and overheating, while operating it at a voltage above its rating can damage the motor.
Current
The current drawn by the oil pump is determined by the power required to drive the pump. The current rating of the electrical components, such as the motor and wiring, must be sufficient to handle the expected current draw.
Power Factor
Power factor is a measure of the efficiency of the electrical system. A low power factor indicates that the electrical system is consuming more reactive power than active power. This can result in increased energy losses and higher operating costs.
Guidelines for Electrical Component Selection
When selecting and sizing electrical components for an oil pump system, the following guidelines should be considered:
- Choose a motor with a voltage rating that matches the voltage supply.
- Select a motor with a current rating that is sufficient to handle the expected current draw.
- Use electrical components with a power factor as close to unity as possible.
- Consider using variable frequency drives (VFDs) to control the pump speed and reduce energy consumption.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
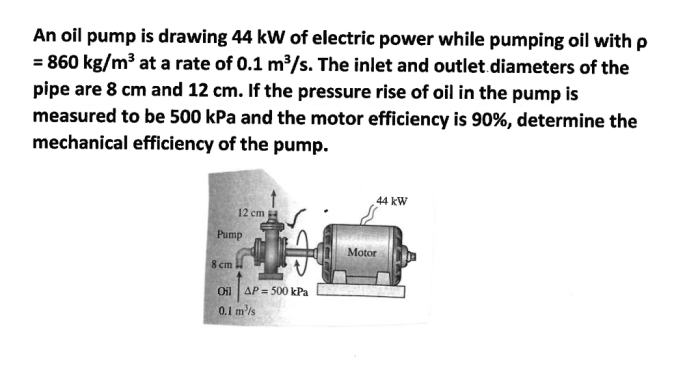
Oil pumps require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and extend their lifespan. Here are some common maintenance procedures and troubleshooting tips:
Lubrication
Oil pumps rely on lubrication to reduce friction and wear. Regular lubrication is crucial to maintain the pump’s efficiency and prevent premature failure. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for the type and frequency of lubrication required.
Inspection
Regular inspections can help identify potential problems early on. Inspect the pump for any leaks, loose connections, or damage. Check the oil level and quality, and replace it if necessary.
Repair
If a problem is identified during inspection or troubleshooting, it is important to address it promptly to prevent further damage. Repairs may involve replacing worn components, tightening loose connections, or addressing leaks. Refer to the manufacturer’s instructions or consult a qualified technician for guidance.
An oil pump drawing 44 kw might not sound like the most inspiring topic, but you’d be surprised. Just like maize cobs in AP art history , even the most mundane subjects can be transformed into something extraordinary with a little creativity.
The intricate patterns and textures found in an oil pump can be just as captivating as the delicate curves of a maize cob. So next time you’re feeling uninspired, take a closer look at your surroundings. You might just be surprised at what you find.
Troubleshooting Power Consumption and Pump Performance
If the oil pump is consuming excessive power or not performing as expected, there may be an underlying issue. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting steps:
- Low Oil Level:Check the oil level and ensure it is at the recommended level. Insufficient oil can lead to increased friction and power consumption.
- Clogged Filter:A clogged filter can restrict oil flow and increase power consumption. Replace the filter as per the manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Worn Bearings:Worn bearings can cause friction and reduce pump efficiency. Replace worn bearings to restore optimal performance.
- Improper Pump Sizing:If the pump is not sized correctly for the application, it may be working harder than necessary, leading to excessive power consumption.
- Electrical Issues:Electrical problems, such as loose connections or faulty wiring, can also affect pump performance and power consumption. Check all electrical connections and components.
Tips for Extending Pump Lifespan and Optimizing Operation
To extend the lifespan of the oil pump and optimize its operation, consider the following tips:
- Follow the manufacturer’s maintenance recommendations and lubrication schedule.
- Use high-quality oil and filters.
- Inspect the pump regularly and address any issues promptly.
- Avoid overloading the pump or operating it under extreme conditions.
- Monitor the pump’s performance and power consumption to identify any potential problems early on.
Applications and Case Studies: An Oil Pump Is Drawing 44 Kw
Oil pumps are indispensable in various industries, ranging from industrial manufacturing to automotive and marine sectors. These pumps play a pivotal role in diverse applications, including lubrication, hydraulic systems, fuel delivery, and cooling.
Power consumption is a crucial factor in the selection and design of oil pumps. It directly impacts the energy efficiency and operating costs of the system. For instance, in the automotive industry, oil pumps are designed to minimize power consumption while ensuring adequate lubrication to critical engine components.
Industrial Applications
- Machinery Lubrication:Oil pumps are used to circulate lubricating oil throughout industrial machinery, reducing friction and wear, and extending the life of components.
- Hydraulic Systems:In hydraulic systems, oil pumps provide the necessary pressure and flow to actuate hydraulic cylinders and motors, enabling precise control of motion and force.
Automotive Applications
- Engine Lubrication:Oil pumps are vital for maintaining adequate oil pressure and flow within the engine, ensuring proper lubrication of moving parts and preventing catastrophic failures.
- Power Steering:Oil pumps provide hydraulic pressure to power steering systems, making it easier to maneuver vehicles.
Marine Applications
- Engine Lubrication:As in automotive applications, oil pumps are essential for lubricating marine engines, ensuring their smooth operation and longevity.
- Bilge Pumping:Oil pumps are used to remove water from the bilge of boats and ships, preventing flooding and potential sinking.
Case Studies
Example 1:A manufacturing plant implemented a new oil pump system that reduced energy consumption by 25%. This resulted in significant cost savings and a reduction in the plant’s carbon footprint.
Example 2:In the automotive industry, a leading car manufacturer redesigned its oil pump to reduce power consumption by 10%. This improvement allowed for better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.
FAQ Corner
What factors affect the energy efficiency of an oil pump?
Pump design, operating conditions, and maintenance practices all influence energy efficiency.
How does power consumption impact pump performance?
Power consumption directly affects pump performance, influencing flow rate, pressure, and head.
What are common maintenance procedures for oil pumps?
Lubrication, inspection, and repair are essential maintenance procedures for oil pumps.