As evidence for evolution pogil answers takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with scholarly precision and authoritative tone, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
From the fossil record to comparative anatomy, from embryology to biogeography, and from natural selection to genetic evidence, this comprehensive exploration delves into the compelling body of evidence that supports the theory of evolution, illuminating the intricate tapestry of life’s history on Earth.
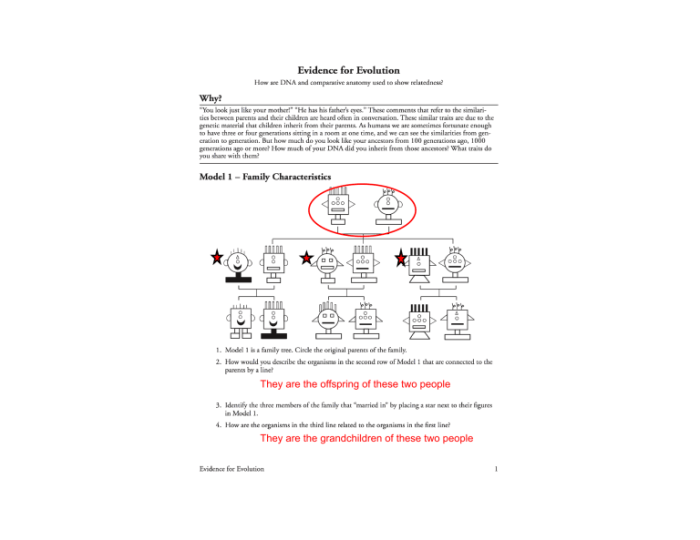
Evidence from Fossils
Fossils are preserved remains or traces of organisms that lived in the past. They provide valuable evidence for evolution as they show the changes that have occurred in species over time.The fossil record demonstrates that species have gradually changed over time.
For example, the fossil record of the horse shows a series of transitional forms from a small, dog-sized animal with three toes to the modern horse with a single hoof.Transitional fossils provide evidence for the gradual change of one species into another.
They show intermediate forms between different species, which support the idea that species have evolved from common ancestors. For instance, the fossil of Archaeopteryx, a bird-like reptile, has features of both reptiles and birds, suggesting that birds evolved from reptilian ancestors.The
discovery of fossils in different geological layers is significant because it provides evidence for the relative ages of different species. Fossils found in lower layers are generally older than those found in higher layers. This allows scientists to construct a timeline of the evolution of species.
Comparative Anatomy: Evidence For Evolution Pogil Answers
Comparative anatomy is the study of the similarities and differences in the anatomy of different organisms. This field of study provides evidence for evolution by showing that different species share similar structures, even if those structures serve different functions.Comparative anatomy has revealed two main types of homologous structures:
- Homologous structuresare structures that have the same basic form and developmental origin but may serve different functions in different species. For example, the forelimbs of humans, bats, and whales are all homologous structures, even though they have evolved to serve different functions such as walking, flying, and swimming.
- Vestigial structuresare structures that have no apparent function in a particular species but are homologous to structures that serve a function in other species. For example, the human tailbone is a vestigial structure that is homologous to the tailbones of other mammals.
Vestigial structures provide evidence for evolution because they suggest that a species has evolved from an ancestor that had a different body plan. For example, the presence of a tailbone in humans suggests that our ancestors had tails at some point in our evolutionary history.Molecular
biology has also provided evidence for evolution by showing that different species share similar DNA sequences. DNA is the genetic material of all living things, and it contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism’s body. By comparing the DNA sequences of different species, scientists can determine how closely related they are.The
more similar the DNA sequences of two species are, the more closely related they are. This is because DNA sequences change over time, and the more time that passes, the more likely it is that two species will have different DNA sequences.The
evidence from comparative anatomy and molecular biology strongly supports the theory of evolution. These fields of study have shown that different species share similar structures and DNA sequences, which suggests that they have evolved from a common ancestor.
Embryology
Embryology, the study of the development of embryos, provides evidence for evolution by revealing similarities in the embryonic stages of different species. This supports the idea that all organisms share a common ancestor.
Recapitulation Theory
The recapitulation theory, also known as the biogenetic law, proposed by Ernst Haeckel in 1866, suggested that the embryonic development of an organism recapitulates, or briefly repeats, the evolutionary history of its species. For example, the human embryo goes through a fish-like stage, a reptile-like stage, and a mammal-like stage before developing into a human.
However, this theory has been largely discredited as an oversimplification of embryonic development.
Similarities in Embryonic Development
Despite the limitations of the recapitulation theory, comparative embryology has revealed striking similarities in the embryonic development of different species. For example:
- All vertebrate embryos develop from a three-layered germ disc: the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- Many animal embryos have a tail at some stage of development.
- The embryos of all mammals, including humans, have pharyngeal arches, which are structures that give rise to the face, neck, and some internal organs.
Significance of Studying Embryology
Studying embryology is significant for understanding evolutionary relationships because it provides insights into the shared ancestry of different species. The similarities in embryonic development suggest that these species have evolved from a common ancestor. By comparing the embryonic stages of different organisms, scientists can trace their evolutionary history and reconstruct the phylogenetic tree of life.
Biogeography
Biogeography studies the distribution of species and ecosystems across the Earth. It provides evidence for evolution by examining patterns of species distribution, continental drift, and the role of adaptation and natural selection in shaping these patterns.
Species Distribution Patterns
- Endemism:Species found only in specific geographic regions, such as the marsupials in Australia, support the idea that species evolve in isolation and adapt to their local environments.
- Disjunct Distributions:Species with similar characteristics found in geographically separated areas, such as the Venus flytrap in North America and South Africa, suggest that these species shared a common ancestor that dispersed and evolved independently.
- Adaptive Radiation:When a group of organisms evolves into diverse forms to occupy different niches within an environment, such as the Darwin’s finches on the Galapagos Islands, it demonstrates the role of natural selection in shaping species distribution.
Continental Drift and Isolation
Continental drift, the movement of Earth’s continents over time, has played a significant role in species distribution. When continents drift apart, populations of the same species can become isolated, leading to speciation. For example, the isolation of South America from Africa resulted in the evolution of unique species, such as the South American monkeys and the African apes.
Adaptation and Natural Selection
Adaptation and natural selection shape species distribution by favoring individuals with traits that increase their survival and reproduction in their specific environment. For instance, desert plants have evolved adaptations to conserve water, such as thick, waxy leaves and reduced leaf area, which allow them to survive in arid conditions.
Evidence from Natural Selection

Natural selection is a fundamental mechanism of evolution that drives the adaptation of populations to their environments. It occurs when individuals with favorable traits have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring.
Variation, Inheritance, and Environmental Pressures
Variation within a population is the raw material for natural selection. Genetic variation arises from mutations, gene flow, and genetic recombination during sexual reproduction. Inherited traits that enhance an individual’s fitness in a particular environment increase the probability of survival and reproductive success.
Environmental pressures, such as predation, competition for resources, and climate change, shape the direction of natural selection. Individuals with traits that provide an advantage in a given environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous genes to future generations.
Antibiotic Resistance in Bacteria
Antibiotic resistance in bacteria is a striking example of the power of natural selection. When bacteria are exposed to antibiotics, individuals with random mutations that confer resistance have a survival advantage. These resistant bacteria proliferate, passing on their resistance genes to their offspring.
Over time, the population of bacteria becomes increasingly resistant to the antibiotic, demonstrating the rapid and potent effects of natural selection in shaping the genetic makeup of a population.
Genetic Evidence
Genetic evidence provides compelling support for the theory of evolution. Genetic mutations and genetic drift are two mechanisms that contribute to genetic variation, which is the raw material for natural selection to act upon. DNA sequencing allows scientists to compare the genetic makeup of different species, providing insights into their evolutionary relationships.
By analyzing genetic data, researchers can reconstruct the history of life on Earth and understand the processes that have shaped the diversity of life forms we see today.
Genetic Mutations, Evidence for evolution pogil answers
Genetic mutations are random changes in the DNA sequence of an organism. These mutations can be caused by a variety of factors, including environmental factors such as radiation and chemicals, and errors during DNA replication. Mutations can have a range of effects, from being neutral to being beneficial or harmful to the organism.
Beneficial mutations can provide an organism with an advantage in its environment, increasing its chances of survival and reproduction. Over time, the accumulation of beneficial mutations can lead to significant evolutionary changes.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is the random change in the frequency of alleles in a population. This can occur due to chance events, such as the loss of individuals from a population due to natural disasters or population bottlenecks. Genetic drift can lead to the loss of genetic variation within a population, and it can also lead to the fixation of certain alleles, even if they are not beneficial to the organism.
Genetic drift is particularly important in small populations, where the effects of chance events are more pronounced.
DNA Sequencing
DNA sequencing is a technique that allows scientists to determine the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. This information can be used to compare the genetic makeup of different species, providing insights into their evolutionary relationships. By comparing the DNA sequences of closely related species, scientists can identify regions of the genome that have been conserved over time, as well as regions that have diverged.
This information can be used to construct phylogenetic trees, which depict the evolutionary relationships between different species.
Role of Genetic Evidence in Understanding the History of Life on Earth
Genetic evidence has played a crucial role in our understanding of the history of life on Earth. By analyzing the genetic makeup of different organisms, scientists have been able to reconstruct the evolutionary relationships between different species and trace the origins of life back to a common ancestor.
Genetic evidence has also been used to study the processes of speciation and extinction, and to understand the factors that have shaped the diversity of life forms on Earth.
Questions Often Asked
What is the significance of transitional fossils in understanding evolution?
Transitional fossils provide crucial evidence for the gradual change of one species into another, bridging the gaps in the fossil record and supporting the theory of evolution.
How does comparative anatomy contribute to the study of evolution?
Comparative anatomy reveals homologous structures and vestigial structures, providing insights into the evolutionary relationships between species and highlighting the common ancestry of diverse organisms.
What role does embryology play in understanding evolutionary relationships?
Embryology supports the theory of evolution through the concept of recapitulation theory, which suggests that embryonic development recapitulates the evolutionary history of a species.
How does biogeography provide evidence for evolution?
Biogeography examines the distribution patterns of species, revealing the role of continental drift and isolation in speciation and supporting the theory of evolution.
What is the importance of natural selection in the process of evolution?
Natural selection is a fundamental mechanism of evolution, driving the adaptation of species to their environments through the interplay of variation, inheritance, and environmental pressures.